Several judgments have been rendered on the scope of granting registration of patent term extension (PTE). Now a judgment regarding the scope of the extended patent right has been rendered for the first time.
Summary of the case
Debiopharm International SA, the plaintiff, owns a patent for an invention titled "Pharmaceutically stable oxaliplatinum preparation". Debiopharm was granted registrations of PTE for the patent based on approvals provided in the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law for "ELPLAT I.V. Infusion Solution" which is oxaliplatin (equal to oxaliplatinum) preparations.
Towa Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, the defendant, manufactured and sold generic drugs of ELPLAT. Debiopharm sought injunction of manufacturing, etc of the defendant's products alleging that the effect of the extended patent right covers the manufacturing and selling of those products.
Issues
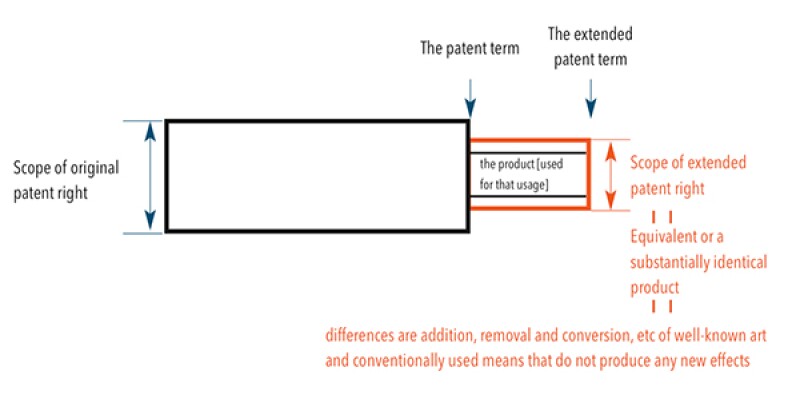
Patent Act Article 68-2 provides that the extended patent right shall not be effective against any act other than the practising of the patented invention for the product which was the subject of the disposition which constituted the reason for the registration of extension (where the specific usage of the product is prescribed by the disposition, the product used for that usage).
Though the effectiveness/efficacy and dosage/administration of the defendant's products are the same as those of ELPLAT, the ingredients are different in that the defendant's products add concentrated glycerin as an additive. Therefore, whether the defendant's products fell under "the product [used for that usage]" became an issue.
Judgment of March 30 2016, Tokyo District Court
The Tokyo District Court (Presiding Judge Shimasue) quoted a purpose of PTE which the Supreme Court and the IP High Court held in the Avastin case and dismissed the claim of Debiopharm.
(1) The effect of the extended patent right: The extended patent right only covers the practising of "the product [used for that usage]" in principle.
However, even though an object product is different from "the product [used for that usage]", it is reasonable to deem that the extended patent right covers the practising of such a product as an equivalent or a substantially identical product of "the product [used for that usage]", where the differences are addition, removal and conversion, etc of well-known art and conventionally used means that do not produce any new effects.
(2) In a case where disposition is an approval for a medicine provided in the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act, "dosage, administration, effectiveness and efficacy", which identify "usage" of the medicine, are inevitably examined. Therefore, the approval falls under "where the specific usage of the product is prescribed by the disposition" in Patent Act Article 68-2 within bracket and it is necessary to identify "product" and "usage" for examining the scope of the extended patent right.
In a case of a patented invention for an ingredient of a medicine, the extended patent right covers the practising of the patented invention identified by "ingredient (not limited to active ingredient) and quantity" as "product" and identified by "effectiveness/efficacy" and "dosage/administration" as "usage".
(3) "The product used for that usage" in this case: The medicine that is the object of the disposition is ELPLAT; therefore "the product used for that usage" is the formulation which includes only "oxaliplatin" and "water for injection" and does not include other ingredients.
The ingredients of the defendant's products include "concentrated glycerin" as an additive other than "oxaliplatin" and "water". The defendant's products differ from "the product used for that usage" in its "ingredients". Therefore, the defendant's products do not fall under "the product used for that usage".
(4) Whether the defendant's products fall under an equivalent or a substantially identical product of "the product used for that usage": If the characteristic part of the invention is only ingredients of medicine such as an invention regarding novel compound or medical use of a specific compound, a product that only differs in ingredient other than active ingredient and has bioequivalence may fall under an equivalent or a substantially identical product of "the product used for that usage" because that difference often falls under addition, etc of well-known art and conventionally used means that do not produce any new effect. Meanwhile, if the characteristic part of the invention is the whole ingredients of a medicine such as an invention regarding formulation, a product which only differs in ingredient other than active ingredient and has bioequivalence sometimes does not fall under a substantially identical product because that difference sometimes does not fall under addition, etc of well-known art and conventionally used means and sometimes produces a new effect.
In this case, oxaliplatinum had been well-known as a substance and in usage as an anti-cancer drug. Therefore, the invention is not characteristic only in active ingredients of the medicine but in all the ingredients of a medicine.
Adding concentrated glycerin to oxaliplatin aqueous solution may not fall under addition etc of well-known art and conventionally used means at the time of starting test necessary for obtaining a disposition for the defendant's products. Instead, it may produce a new effect which added glycerin inhibits decomposition of oxalipratin.
Therefore, the defendant's products do not fall under an equivalent or a substantially identical product of "the product used for that usage".
Practical tips
This is the first judgment that rendered a concrete ruling regarding the scope of the extended patent right as not dictum but ratio decidendi. This judgment specifically ruled on the criteria of an equivalent or a substantially identical product.
According to this judgment, the scope of the extended patent right often covers accused products regarding an invention whose characteristic part is only ingredients of medicine (a substance patent or a use patent etc) and does not often cover them regarding an invention whose characteristic part is the whole ingredients of a medicine (a formulation patent etc).
However, there seems to be not so many cases where a scope of the former patent right becomes an issue when generic drugs enter into a market because the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare is supposed not to grant approval for generic drugs when a product patent or a use patent exists. Meanwhile, in the latter case, there is a possibility that generic drugs avoid an effect of the extended patent right by changing an additive of the generic drugs and making into a formulation which shows a new effect. It had been expected that the Avastin Supreme Court's judgment results in the situation that the scope of granting registration of PTE becomes broader whereas the scope of the extended patent right becomes narrower. This expectation has come true.
Attention must be paid to the IP High Court judgment.

|

|
Takanori Abe |
Michiko Kinoshita |
ABE & PartnersMatsushita IMP Building1-3-7, Shiromi, Chuo-ku, Osaka, 540-0001, JapanTel: +81 6 6949 1496Fax: +81 6 6949 1487abe@abe-law.comwww.abe-law.com









