According to the Trademark Examination Guideline of the Turkish Patent and Trademark Office, which is aligned with the EUIPO guidelines, the comparison of trademarks should be based on the overall impression created by the marks. In this assessment, the length of a trademark can be an important factor. In general, the shorter a sign is, the easier it is for the public to perceive each of its elements. Conversely, in longer signs, differences are less likely to be noticed. That said, each case must be assessed individually, taking all relevant circumstances into account.
The Turkish Court of Cassation (CoC) follows the same general approach in its decisions. However, it can be observed that the CoC tends to place greater weight on the main elements of the trademarks, even when the marks are short. The court’s established position on short-word marks is that the focus should remain on the dominant element. As long as the main elements are identical or highly similar, the presence of additional elements is usually not sufficient to eliminate the likelihood of confusion.
For example, in its previous decision dated June 20 2023, with merit No. 2022/954 and decision No. 2023/3909, the CoC upheld the Regional Court’s decision, finding the trademarks listed below to be confusingly similar.
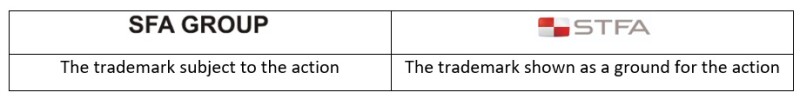
In the upheld decision, the Regional Court highlighted that the main element of the subject trademark is the phrase “SFA”, which differs by only a single letter from the trademark featuring the phrase “STFA” as its main element. The court concluded that, given the high similarity between the main elements of the disputed trademarks and the similarity of the goods and services covered by them, there exists a likelihood of confusion between these trademarks.
Likewise, consistent with its previous decisions, a CoC decision dated March 3 2025, with merit No. 2024/3305 and decision No. 2025/1446, upheld the Regional Court’s decision regarding the similarity of the below marks, which had rescinded the first-instance court’s decision.
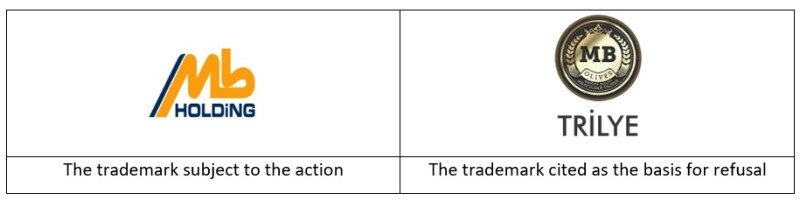
In its decision, despite the first-instance court having found these trademarks dissimilar, the Regional Court carefully identified the primary and secondary elements of the disputed trademarks and concluded that the main elements of both trademarks are the phrase “MB”. Consequently, the court determined that the addition of the phrase “Holding”, which lacks distinctiveness, together with the stylisation of the phrase “MB”, was deemed insufficient to differentiate the above-left trademark from the trademark cited as the basis for refusal.
It is therefore essential to consider whether the additional elements added to short-word trademarks are descriptive, as well as the positioning of the short-word elements within the trademarks. Despite visual differences between the trademarks, the presence of the same main element was deemed sufficient to establish similarity and a likelihood of confusion.
Key takeaways on short-word trademarks
As can be observed from the relevant decisions and the CoC’s approach, in the assessment of similarity for short-word trademarks – even those consisting of just two letters – the main elements of the marks play a decisive role, whereas differences in secondary elements alone are not sufficient to differentiate the marks. While this approach has long been adopted in numerous disputes, each case has its own unique characteristics and different outcomes remain possible in individual disputes.













