Many food products contain known ingredients, rather than novel ingredients, as essential components. Such food products are usually a result of combining components in a special ratio to achieve a particular flavour, taste, effect, etc.
Claim format
Inventions for food products are commonly drafted as method or composition claims to secure a patent in Korea. For example, a method of enhancing the flavour of a food product by uniformly mixing substance A with sodium glutamate, and a food composition for lowering blood glucose level comprising substance A as an active ingredient.
Natural products per se are not patentable because they are already known in the art and thus lack novelty. However, if one natural product shows a unique function or effect, a "use invention" for the natural product may be permitted as a patent as long as it satisfies the patentability requirements.
When one drafts a patent specification and claims for food-related inventions, the following should be kept in mind.
Description in the specification and claims
In the specification, it is necessary to describe (i) the sensory effects of the food (i.e. appearance, taste, smell, texture, etc.), and/or (ii) functional effects of the food.
The sensory effects must be objectively and scientifically demonstrated using chemical or mechanical analysis (e.g. electronic nose, electronic tongue, and texture profile analyser), a systematic sensory test, etc. Trained panels can be used for sensory testing to determine people's food preference.
In the case of functional foods, experimental data verifying the effectiveness or utility should be disclosed in the specification originally filed, in a similar way to medical use inventions. Such data can be obtained from in vitro, animal, or human tests, or a method using a biomarker. Unlike medical use inventions, qualitative analysis or sensory test results for food products are acceptable to the Korean Intellectual Property Office (KIPO).
Claims for functional foods are usually written in the form of "a food composition for improving or preventing…", and are not allowed to use the expression "treatment" or "treating", which indicates medical utility. The use of a food composition is required for the object achieved by the property of functional components, such as lowering blood glucose level, improving obesity, and improving hyperlipidemia.
Overall, it seems that a lower standard for the specification and claims is applied to food-related inventions than for medical use inventions.
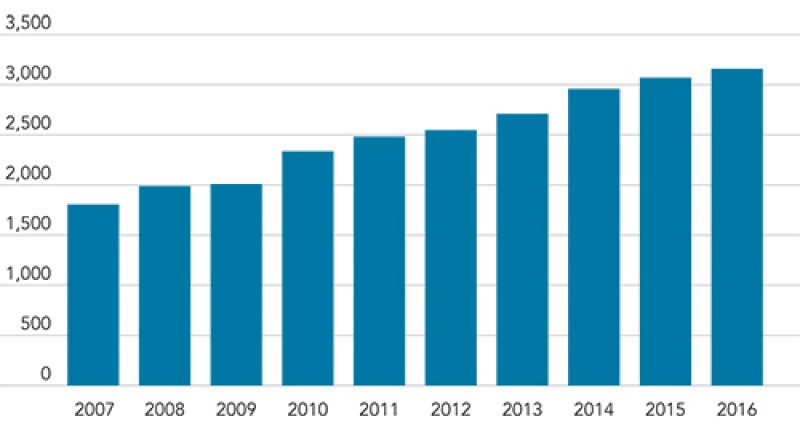
Trends in patent application filing for food-related inventions for the last 10 years in Korea
Safety aspect
As food is ingested, safety to the human body should not be overlooked. In a case in which it is not obvious to a person skilled in the art whether materials or components constituting a food composition are safe for human consumption, the composition claim is rejected as an invention likely to cause harm to public health under Article 32 of the Korean Patent Act. According to KIPO's Examination Guidelines (a) materials obtained from a human body (e.g. placenta and blood) and (b) substances toxic or harmful to the human body (e.g. DDT and Hg) are not permitted for use in the preparation of food. When the KIPO raises a rejection on the ground that the safety of components of a food composition is unknown, the rejection can be resolved by submitting a test result to prove human safety.
Patent application filings for food-related inventions are continuously increasing in Korea, as shown in the graph above. We believe that careful preparation of the specification and claims raises the chance of securing a patent for food-related inventions.
Min Son
Partner, Hanol IP & Law
HANOL Intellectual Property & Law
6th Floor, Daemyung Tower, 135, Beobwon-ro, Songpa-gu
Seoul, 05836
Republic of Korea
Tel: +82 2 942 1100
Fax: +82 2 942 2600












